Chapter4 Boolean Algebra & Logical Simplification
Boolean Operations and Expressions
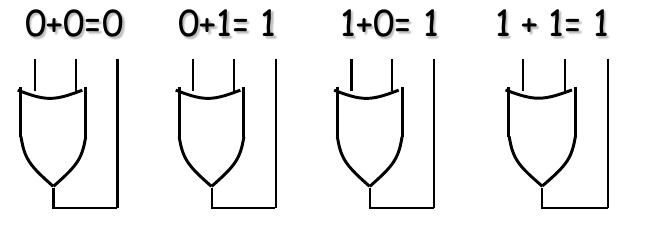
- Boolean addition is equivalent to the OR operation and the basic rules are illustrated with their relation to the OR gates as follows:
- A sum term is equal to 1 when one or more of the literals in the term are 1.
- A sum term is equal to 0 only if each of the literals is 0.
-
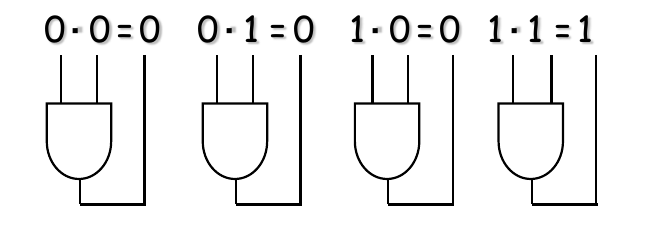
Boolean multiplication is equivalent to the AND operation and the basic rules are illustrated with their relation to the AND gates as follows:
- A product term is equal to 1 only if each of the literals in the term are 1.
- A product term is equal to 0 when one or more of the literals is 0.
![image-20250505204913948]()
Laws and Rules of Boolean Algebra
Commutative, Associative and Distributive Law
| 序号 | 定律 (Laws) | 布尔表达式 (Boolean Expression) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Commutative law of addition 加法交换律 | |
| 1 | Commutative law of multiplication 乘法交换律 | |
| 2 | Associative law of addition 加法结合律 | |
| 2 | Associative law of multiplication 乘法结合律 | |
| 3 | Distributive law 分配律 |
常用运算公式
Boolean Analysis of a logic Circuit
Constrcting the truth table for a logic circuit
- 先判断表有几行,大概长什么样(n个输入就有种情况)
- 建议使用逻辑判断的方法把输出为0/1的输入(选简单的算)一步步找出来
- 表达式比较复杂,逻辑判断不方便的话,那就老老实实一个个算!
Standard Forms of Boolean Expressions
- Sum-of-Products Form (SOP Form)
- Product-of-Sums Form (POS Form)
- Standard SOP Form
- Standard POS Form
Conversion of a General Expression to SOP Form
- Any logic expression can be changed into SOP form by applying Boolean algebra techniques.
- 使用下面这个式子,把积项中所有缺失的项全部补出来(拆出来)
Some Concepts
- Normal Product Term: Product term with no repeated variables.
- Minterm over N Variables: Normal product term with N variables
The Standard SOP Form
- Standard SOP Form: Sum of min-terms Form
Converting Product Terms to Standard SOP
- 识别缺失变量:对于一个非标准的积项,确定表达式域中哪些变量是缺失的。
- 乘以包含缺失变量的和项:将该非标准积项乘以一个由“缺失变量 + 其补数”构成的和项(例如,如果变量 ‘D’ 缺失,则乘以 )。根据布尔代数规则 ,这样做不会改变积项的逻辑值。应用分配律后,这将产生两个新的积项。
- 重复:对新产生的积项,重复步骤1和2,处理任何仍然缺失的变量,直到所有得到的积项都包含域中的所有变量(以原变量或补数形式出现)。
Binary Representation of a Standard Product Term
- A Standard Product term is equal to 1 for only one combination of variable values.
- So the product term has a binary value of 1010,
- For minterm: 1 is variable, 0 is complement
- An SOP expression is equal to 1 only if one or more of the product terms in the expression is equal to 1.
POS Form
- Sum Term: A single literal or a sum (OR) of 2 or more literals.
- Product of Sums: Logical product of sum terms.
- Normal Sum Term: Sum term with no repeated variables.
- Maxterm over N variables: Normal sum term with N variables
The Standard POS Form
- Standard POS Form is Product of Maxterms Form
Conversion of a Sum Term to Standard POS
- 识别缺失变量:对于一个非标准的和项,确定表达式域中哪些变量是缺失的。
- 添加缺失变量的积项:在非标准的和项中,加上一个由缺失变量及其补数组成的积项(例如,如果变量 缺失,则加上 )。根据布尔代数规则 ,添加这个积项不会改变和项的逻辑值。
- 应用分配律:使用布尔代数规则 来分解表达式,得到两个和项。
- 重复:对新产生的和项,重复步骤1-3,处理任何仍然缺失的变量,直到每个和项都包含域中的所有变量(以原变量或补数形式出现)。
Binary Representation of a Standard Sum Term
- 一个标准和项(也称为 Maxterm,最大项)只在唯一一种变量取值组合下等于 。
- 其二进制表示的规则是:
- 变量的原形式(如 )对应二进制值 。
- 变量的补数形式(如 )对应二进制值 。
- 例如,标准和项 对应的二进制值是 。当输入变量为 时,该和项的值为 。
- 一个标准的和之积(POS)表达式,只要其包含的任何一个标准和项等于 ,整个表达式的值就为 。
Conversion Between Different Forms
Convertincg Standard SOP to Standard POS
-
SOP和POS,即最大项和最小项是互补的
- 利用这一点进行计算
- SOP中的最大项和POS中的最小项
-
The binary values of the product terms in a given standard SOP expression are not present in the equivalent standard POS expression.
-
Also, the binary values that are not represented in the SOP expression are present in the equivalent POS expression.
So, the steps are:
-
Evaluate each product term in the SOP expression. That is, determine the binary numbers which represent the product terms.
-
Determine all of the binary numbers not included in the evaluation in step 1
-
Write the equivalent sum term for each binary number from step 2 and express in POS form.
-
For minterm: 1 is variable, 0 is complement
-
For maxterm: 1 is complement, 0 is variable
-
Logic function Simplification
没啥好写的,灵活应用前面说的公式,将表达式尽可能化到最简
卡诺图(The Karnaugh Map)
- 定义与用途: 卡诺图(Karnaugh Map)是一种图形化的方法,用于简化布尔表达式。它利用人脑的模式识别能力来寻找最简化的逻辑表达式。卡诺图类似于真值表,展示所有可能的输入变量组合及其对应的输出。
- 结构: 卡诺图是一个单元格阵列,每个单元格对应一个输入变量组合。单元格的排列遵循格雷码顺序,使得相邻单元格之间只有一个变量发生变化。
- 相邻性:
- 物理上相邻(上下左右)的单元格是相邻的。
- 顶行与底行对应的单元格相邻。
- 最左列与最右列对应的单元格相邻。
- 变量数量: 卡诺图对于简化最多六个变量的表达式非常有效。对于更多变量,模式识别会变得困难。常见的有 2 变量、3 变量、4 变量和 5 变量卡诺图。
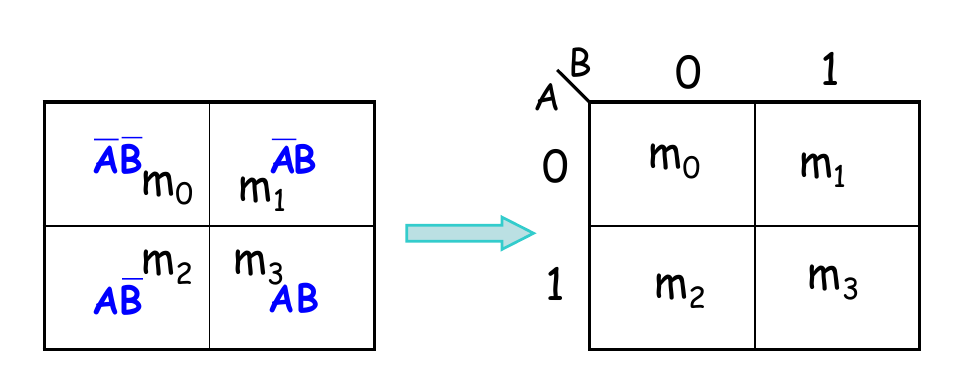
2-5变量卡诺图基本形式
2变量
3变量
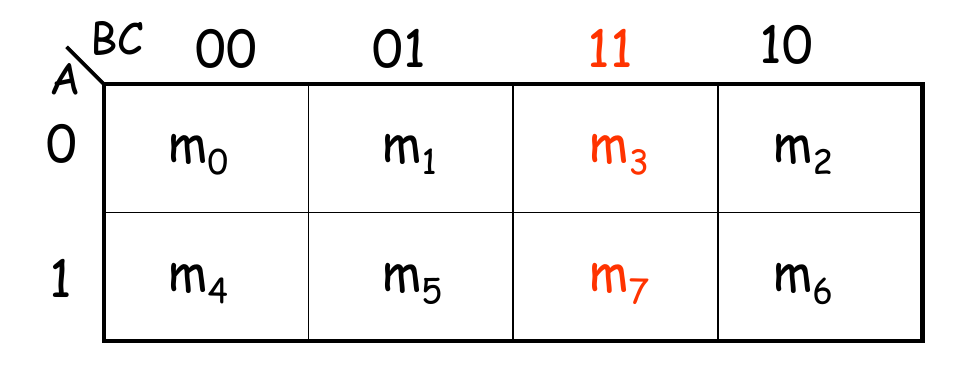
4变量
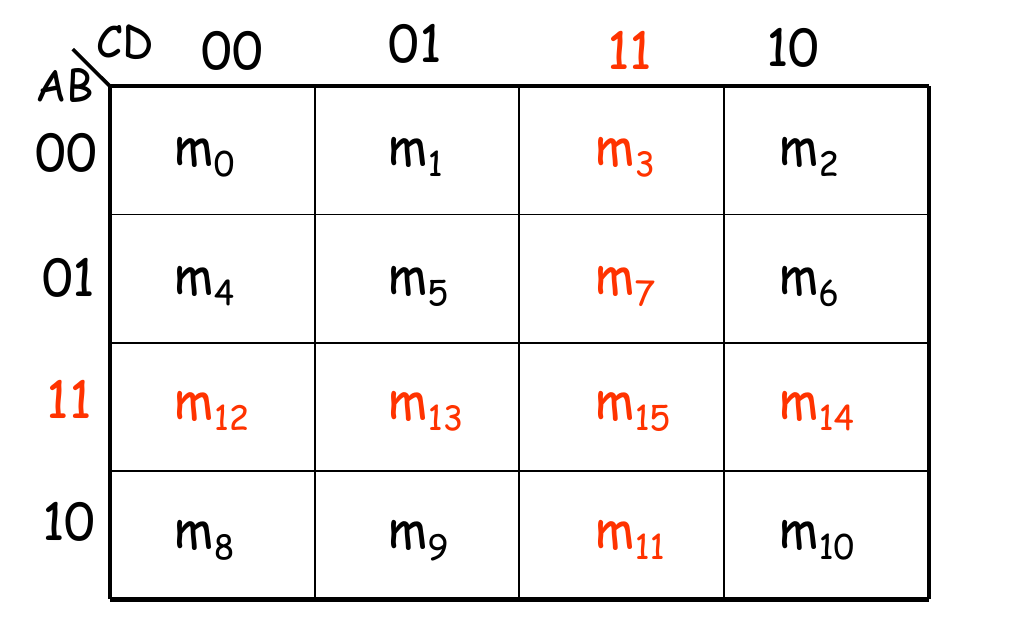
5变量
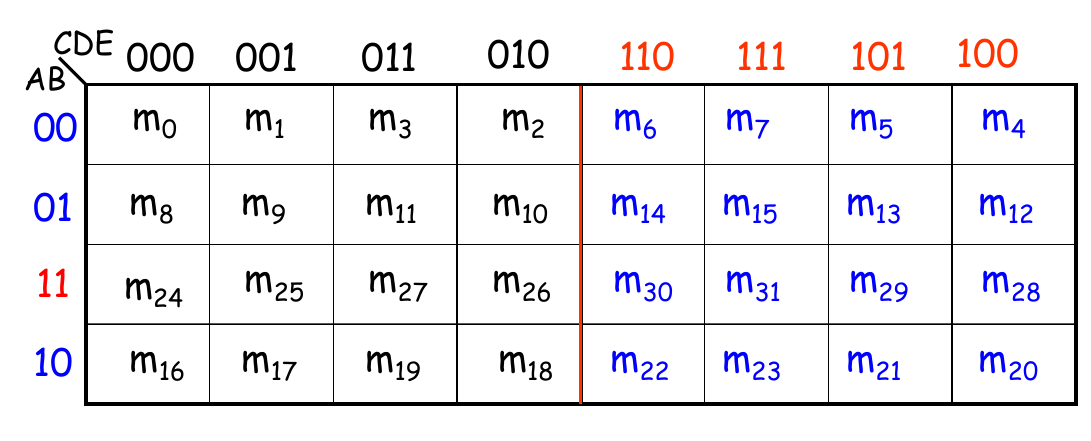
5变量卡诺图有两种形式,注意:这两种形式在看相邻单元格时的方法是不同的
- 上面这种用C=0/1分左右的卡诺图,看相邻项的时候沿着中间这条红线把纸面对折(或者也可以说,右面以中心红线为轴翻转180),左右两部分叠在一起,上下相邻的单元格是相邻的
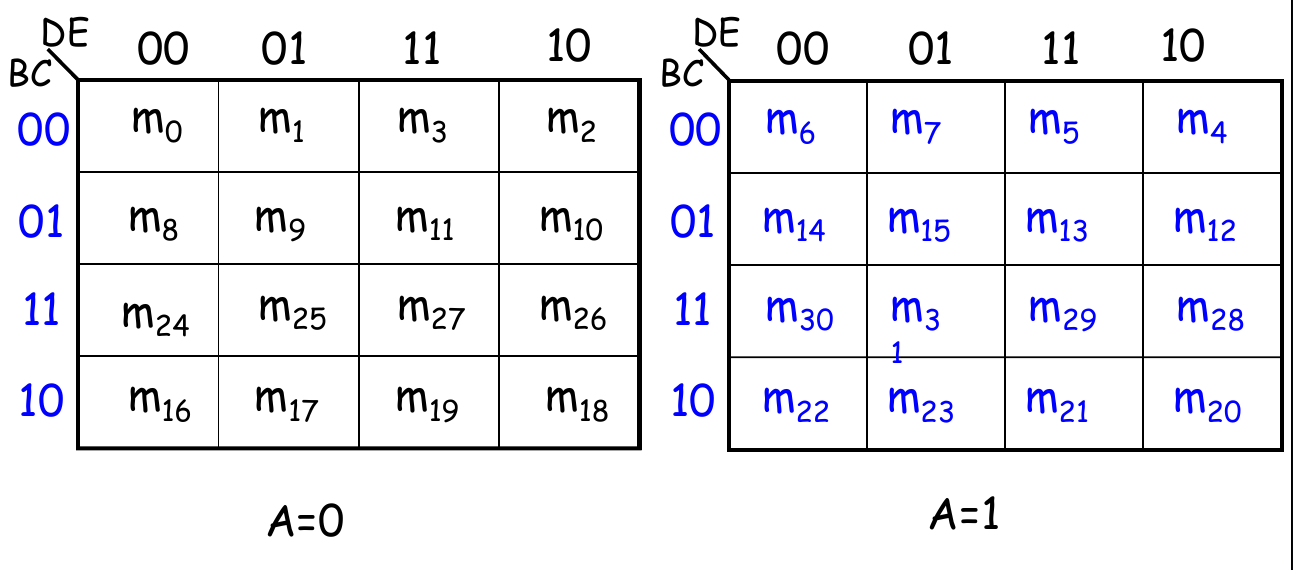
- 下面这种用A=0/1分左右的卡诺图,看相邻项的时候把左右两部分直接上下重叠即可(单元格相互对应),不要翻转
使用卡诺图进行逻辑简化 (SOP - 积之和)
- 映射标准 SOP 表达式:
- 确定标准 SOP 表达式中每个乘积项的二进制值。
- 在卡诺图上对应二进制值的单元格中标注 1。地图上 1 的数量等于标准 SOP 表达式中乘积项的数量。未标注 1 的单元格对应表达式值为 0 的情况 [cite: 35]。
- 映射非标准 SOP 表达式: 将非标准的 SOP 表达式的每个项扩展(补全缺失变量),然后在卡诺图上标记所有对应的单元格为 1。
- 寻找最大分组 (Grouping):
- 目标是最大化分组的大小并最小化分组的数量。
- 分组必须包含 1, 2, 4, 8 或 16 个单元格。
- 组内的每个单元格必须与同组的至少一个其他单元格相邻。
- 尽可能圈出最大的分组 [cite: 46]。
- 确保地图上所有的 1 都至少被一个分组包含。不允许 L 型或 U 型分组。
- 确定最小项:
- 对于每个分组,找出在分组内保持不变的变量。那些在组内既有原变量又有反变量形式出现的变量将被消去。
- 根据分组大小确定最小乘积项 [cite: 51]:
- 1 单元格组 -> n 变量乘积项 (n 为总变量数)
- 2 单元格组 -> (n-1) 变量乘积项
- 4 单元格组 -> (n-2) 变量乘积项
- 8 单元格组 -> (n-3) 变量乘积项
- 求和: 将所有分组对应的最小乘积项相加(逻辑或),得到最简 SOP 表达式。
使用卡诺图进行逻辑简化 (POS - 和之积)
- 映射标准 POS 表达式:
- 确定标准 POS 表达式中每个和项的二进制值(使该和项为 0 的值)。
- 在卡诺图上对应二进制值的单元格中标注 0。
- 分组与简化:
- 过程与 SOP 类似,但是是分组 0 而不是 1。
- 目标是圈出包含 1, 2, 4, 8 或 16 个 0 的最大分组。
- 为每个分组确定最小和项(找出组内保持不变的变量,取反变量形式则保留反变量,取原变量形式则保留原变量,然后相加)。
- 将所有分组对应的最小和项相乘(逻辑与),得到最简 POS 表达式。
无关项 (Don’t Care Terms)
- 定义: 输入变量的一种组合,其对应的输出可以是 0 也可以是 1。通常出现在某些输入组合不可能发生,或者发生了但我们不关心其输出值的场合。
- 应用: 在卡诺图上用 ‘X’ 标记。进行分组时,可以将 ‘X’ 视作 1(简化 SOP 时)或 0(简化 POS 时),以帮助形成更大的分组,从而得到更简化的表达式。